Human Authentication From Ankle Motion Data Using Convolutional Neural Networks
– Published in: 2016 IEEE Statistical Signal Processing Workshop (SSP)
– Authors: Matteo Gadaleta, Luca Merelli, Michele Rossi
| Paper Overview |
Goal: Use an ankle-worn inertial measurement unit (IMU) to authenticate users from their gait signatures.
- The authors present a framework integrates gyroscope information with accelerometer signal to get more accurate authentication result.
- Use Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) as universal feature extractors, combination with a one-class classifier based on a Support Vector Machine (SVM).
- With a sequential decision maker that uses the scores outputted by the SVM across subsequent walking cycles.
|
| System Model |
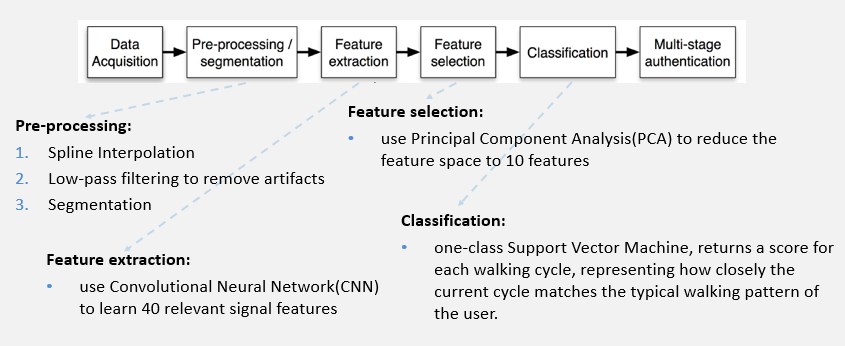 |
| Feature Extraction (Convolutional Neural Networks) |
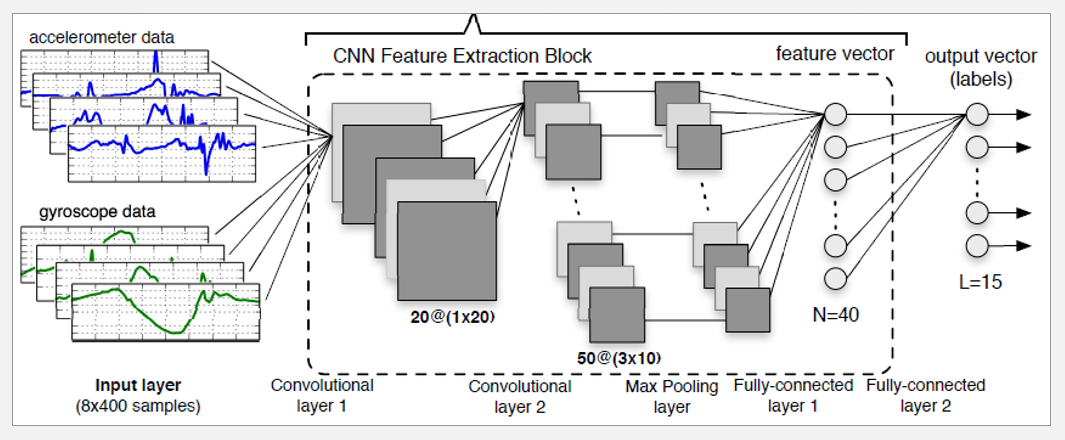
- First convolutional layer: use linear activation functions to perform a preliminary (linear) filtering of the input signals.
- Second convolutional layer: introduce non-linearity through a tanh activation function.
- The max pooling layer: cuts down by half the number of output elements with respect to those in the second convolutional layer.
- Full-connected layer: output a feature vector.
- The last layer employs a softmax function..
|
| Conclusion |
- Proposed an authentication framework that uses accelerometer and gyroscope data acquired from ankle-worn Inertial Measurement Units (IMU).
- It features a cascade of processing tools including, walking cycle segmentation, a convolutional neural network for feature extraction, a one-class classifier based on support vector machines and a sequential decision maker.
- Allowing the identification of the user in fewer than 5 steps and with false positive/negative rates smaller than 1%
|


